Annotation quality & Honeypot
In CVAT, it’s possible to evaluate the quality of annotation through the creation of a Ground truth job, referred to as a Honeypot. To estimate the task quality, CVAT compares all other jobs in the task against the established Ground truth job, and calculates annotation quality based on this comparison.
Note that quality estimation only supports 2d tasks. It supports all the annotation types except 2d cuboids.
Note that tracks are considered separate shapes and compared on a per-frame basis with other tracks and shapes.
See:
- Ground truth job
- Managing Ground Truth jobs: Import, Export, and Deletion
- Assessing data quality with Ground truth jobs
- Annotation quality & Honeypot video tutorial
Ground truth job
A Ground truth job is a way to tell CVAT where to store and get the “correct” annotations for task quality estimation.
To estimate task quality, you need to create a Ground truth job in the task, and annotate it. You don’t need to annotate the whole dataset twice, the annotation quality of a small part of the data shows the quality of annotation for the whole dataset.
For the quality assurance to function correctly, the Ground truth job must have a small portion of the task frames and the frames must be chosen randomly. Depending on the dataset size and task complexity, 5-15% of the data is typically good enough for quality estimation, while keeping extra annotation overhead acceptable.
For example, in a typical task with 2000 frames, selecting just 5%, which is 100 extra frames to annotate, is enough to estimate the annotation quality. If the task contains only 30 frames, it’s advisable to select 8-10 frames, which is about 30%.
It is more than 15% but in the case of smaller datasets, we need more samples to estimate quality reliably.
To create a Ground truth job, do the following:
-
Create a task, and open the task page.
-
Click +.
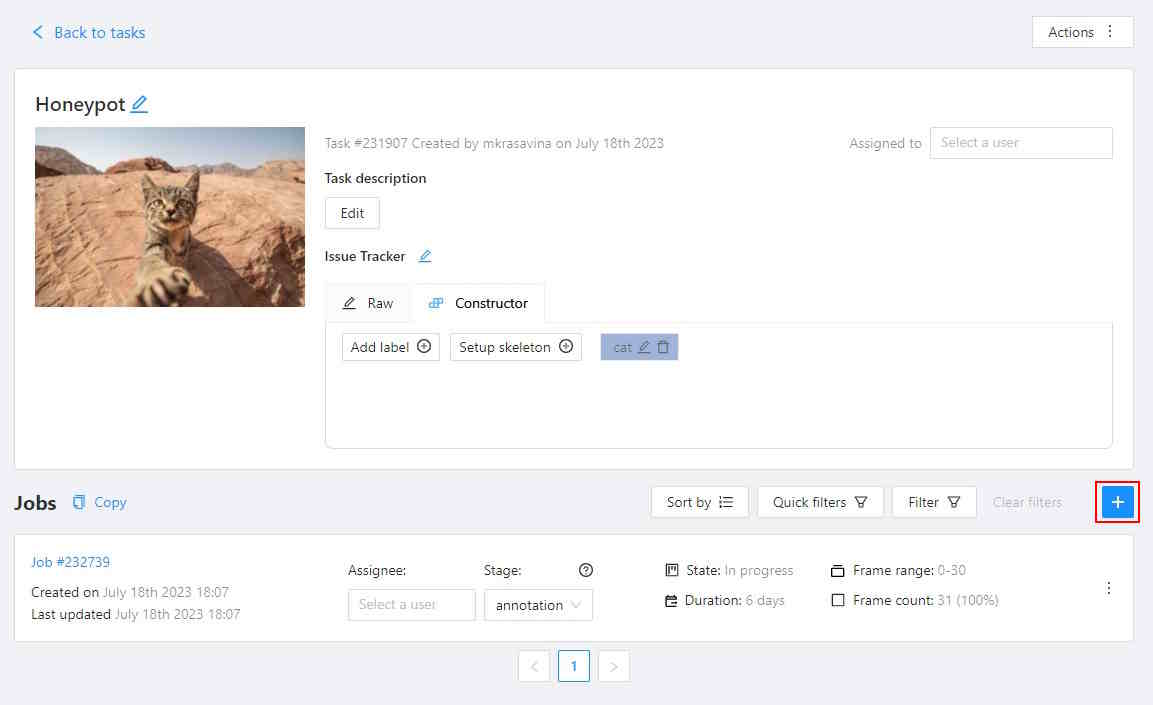
-
In the Add new job window, fill in the following fields:
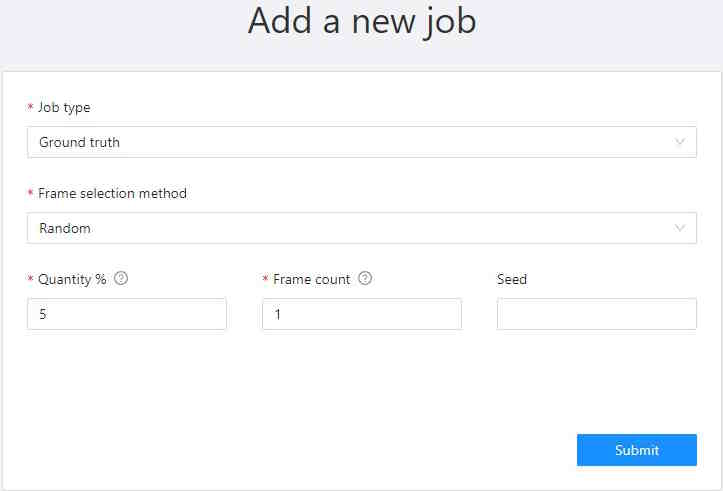
- Job type: Use the default parameter Ground truth.
- Frame selection method: Use the default parameter Random.
- Quantity %: Set the desired percentage of frames for the Ground truth job.
Note that when you use Quantity %, the Frames field will be autofilled. - Frame count: Set the desired number of frames for the “ground truth” job.
Note that when you use Frames, the Quantity % field will be will be autofilled. - Seed: (Optional) If you need to make the random selection reproducible, specify this number.
It can be any integer number, the same value will yield the same random selection (given that the
frame number is unchanged).
Note that if you want to use a custom frame sequence, you can do this using the server API instead, see Jobs API #create.
-
Click Submit.
-
Annotate frames, save your work.
-
Change the status of the job to Completed.
-
Change Stage to Accepted.
The Ground truth job will appear in the jobs list.
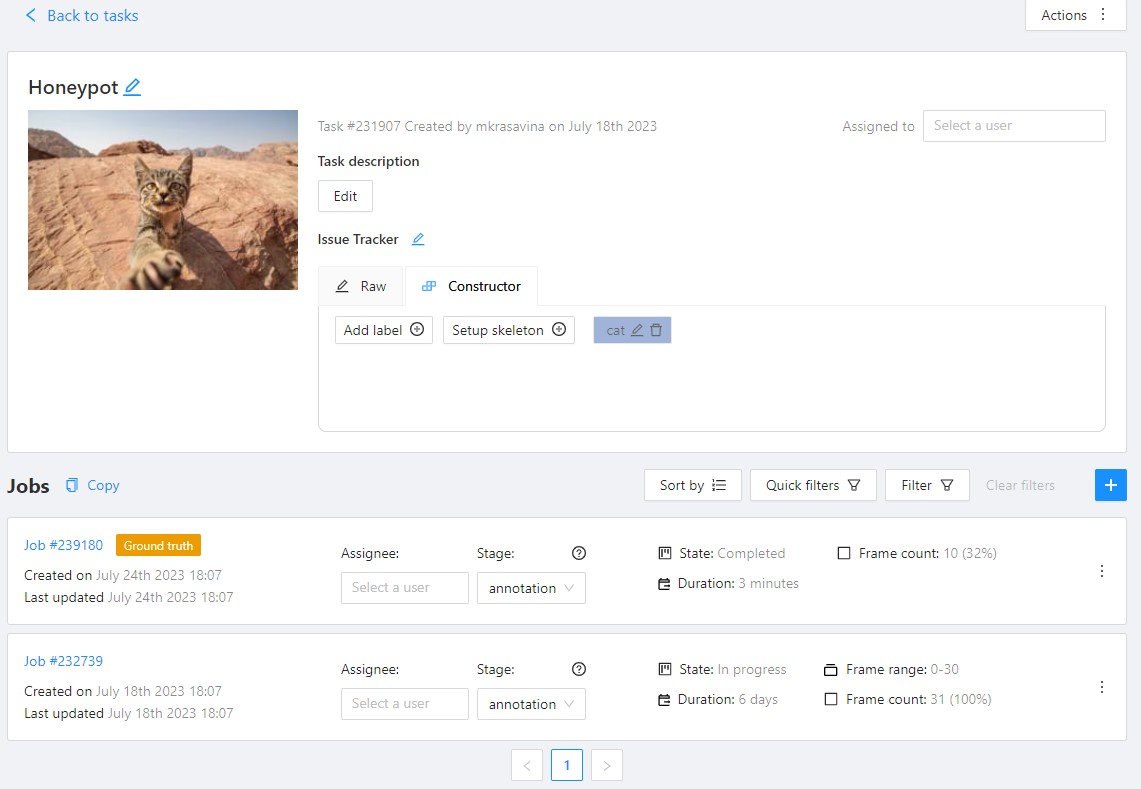
Managing Ground Truth jobs: Import, Export, and Deletion
Annotations from Ground truth jobs are not included in the dataset export, they also cannot be imported during task annotations import or with automatic annotation for the task.
Import, export, and delete options are available from the job’s menu.
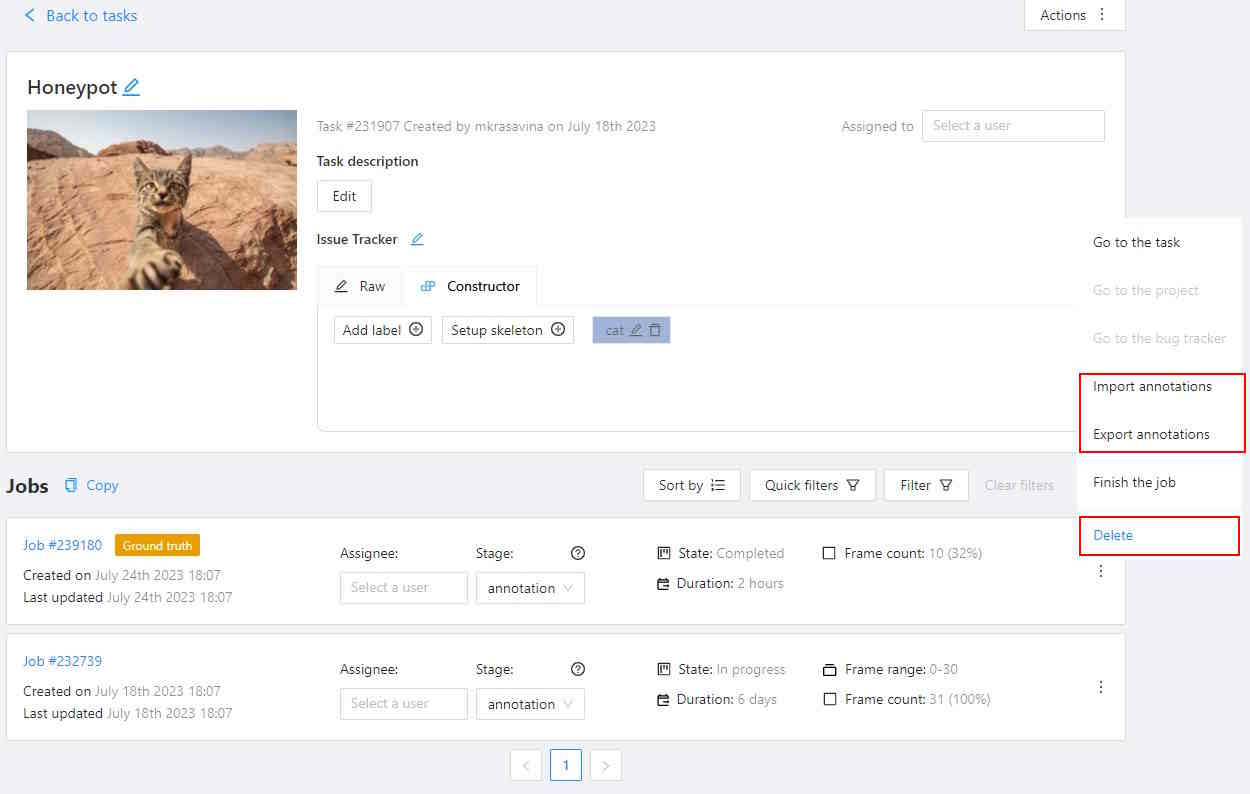
Import
If you want to import annotations into the Ground truth job, do the following.
- Open the task, and find the Ground truth job in the jobs list.
- Click on three dots to open the menu.
- From the menu, select Import annotations.
- Select import format, and select file.
- Click OK.
Note that if there are imported annotations for the frames that exist in the task, but are not included in the Ground truth job, they will be ignored. This way, you don’t need to worry about “cleaning up” your Ground truth annotations for the whole dataset before importing them. Importing annotations for the frames that are not known in the task still raises errors.
Export
To export annotations from the Ground truth job, do the following.
- Open the task, and find a job in the jobs list.
- Click on three dots to open the menu.
- From the menu, select Export annotations.
Delete
To delete the Ground truth job, do the following.
- Open the task, and find the Ground truth job in the jobs list.
- Click on three dots to open the menu.
- From the menu, select Delete.
Assessing data quality with Ground truth jobs
Once you’ve established the Ground truth job, proceed to annotate the dataset.
CVAT will begin the quality comparison between the annotated task and the
Ground truth job in this task once it is finished (on the acceptance stage and in the completed state).
Note that the process of quality calculation may take up to several hours, depending on the amount of data and labeled objects, and is not updated immediately after task updates.
To view results go to the Task > Actions > View analytics> Performance tab.
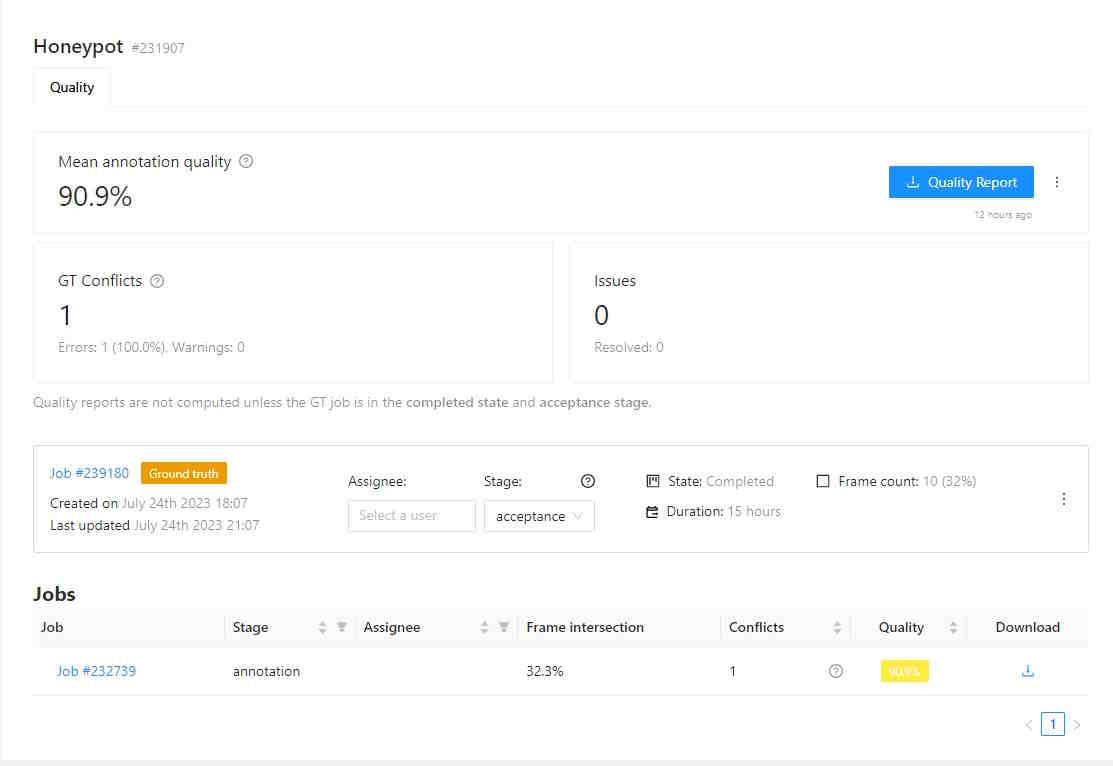
Quality data
The Analytics page has the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Mean annotation quality | Displays the average quality of annotations, which includes: the count of accurate annotations, total task annotations, ground truth annotations, accuracy rate, precision rate, and recall rate. |
| GT Conflicts | Conflicts identified during quality assessment, including extra or missing annotations. Mouse over the ? icon for a detailed conflict report on your dataset. |
| Issues | Number of opened issues. If no issues were reported, will show 0. |
| Quality report | Quality report in JSON format. |
| Ground truth job data | “Information about ground truth job, including date, time, and number of issues. |
| List of jobs | List of all the jobs in the task |
Annotation quality settings
If you need to tweak some aspects of comparisons, you can do this from the Annotation Quality Settings menu.
You can configure what overlap should be considered low or how annotations must be compared.
The updated settings will take effect on the next quality update.
To open Annotation Quality Settings, find Quality report and on the right side of it, click on three dots.
The following window will open. Hover over the ? marks to understand what each field represents.
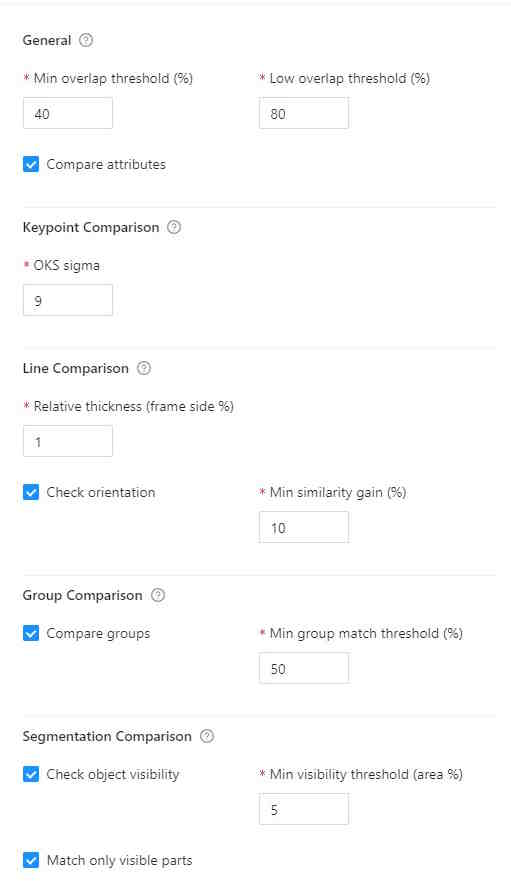
Annotation quality settings have the following parameters:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Min overlap threshold | Min overlap threshold(IoU) is used for the distinction between matched / unmatched shapes. |
| Low overlap threshold | Low overlap threshold is used for the distinction between strong/weak (low overlap) matches. |
| OKS Sigma | IoU threshold for points. The percent of the box area, used as the radius of the circle around the GT point, where the checked point is expected to be. |
| Relative thickness (frame side %) | Thickness of polylines, relative to the (image area) ^ 0.5. The distance to the boundary around the GT line inside of which the checked line points should be. |
| Check orientation | Indicates that polylines have direction. |
| Min similarity gain (%) | The minimal gain in the GT IoU between the given and reversed line directions to consider the line inverted. Only useful with the Check orientation parameter. |
| Compare groups | Enables or disables annotation group checks. |
| Min group match threshold | Minimal IoU for groups to be considered matching, used when the Compare groups are enabled. |
| Check object visibility | Check for partially-covered annotations. Masks and polygons will be compared to each other. |
| Min visibility threshold | Minimal visible area percent of the spatial annotations (polygons, masks). For reporting covered annotations, useful with the Check object visibility option. |
| Match only visible parts | Use only the visible part of the masks and polygons in comparisons. |
GT conflicts in the CVAT interface
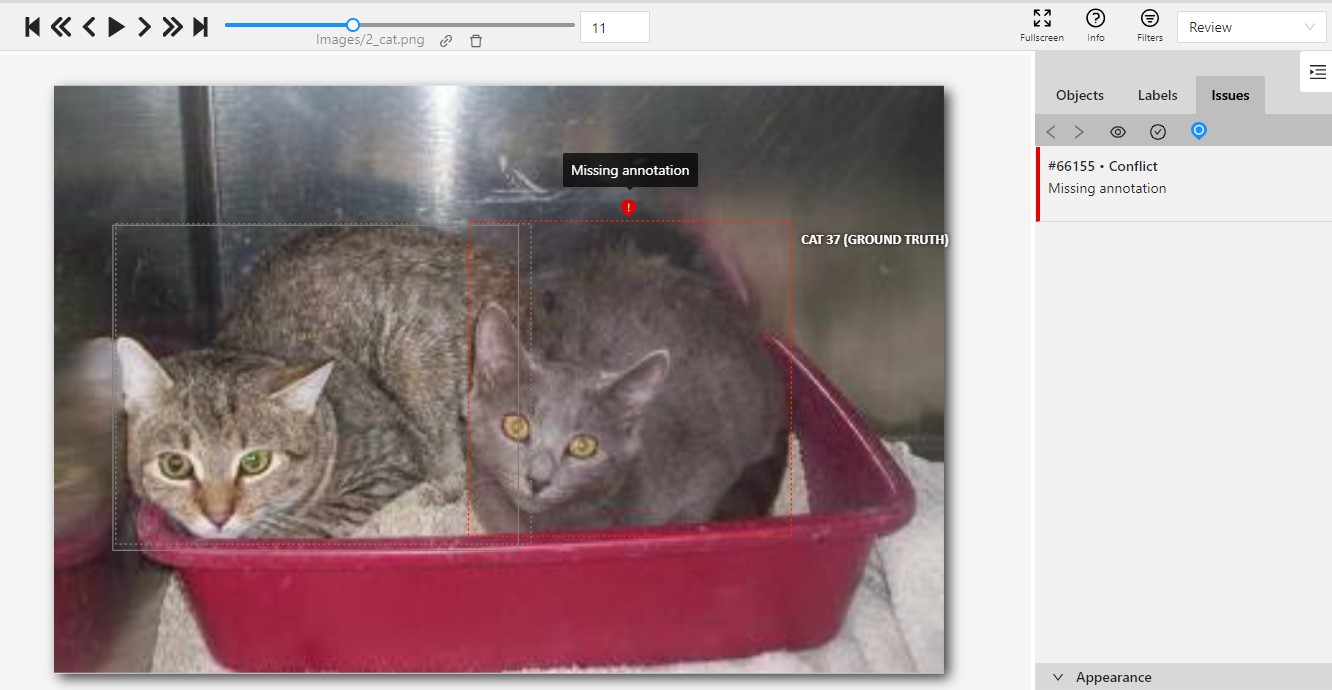
To see GT Conflicts in the CVAT interface, go to Review > Issues > Show ground truth annotations and conflicts.
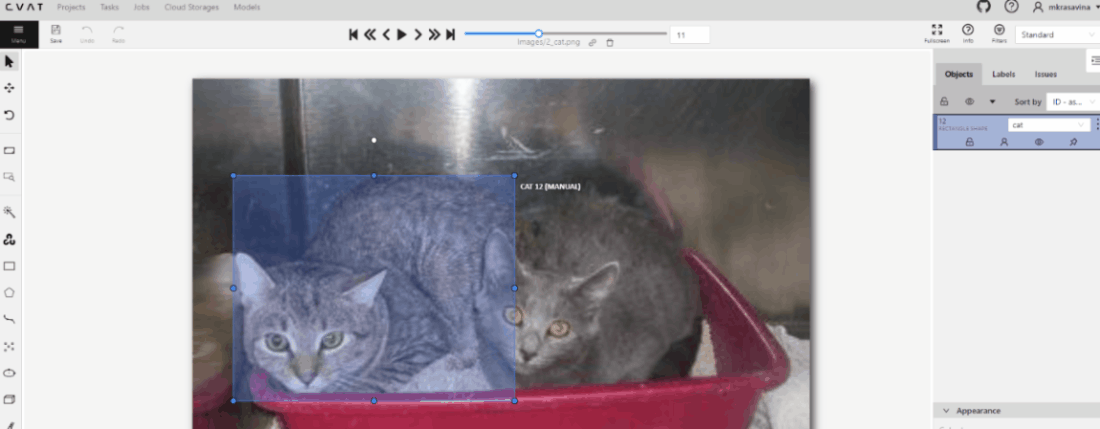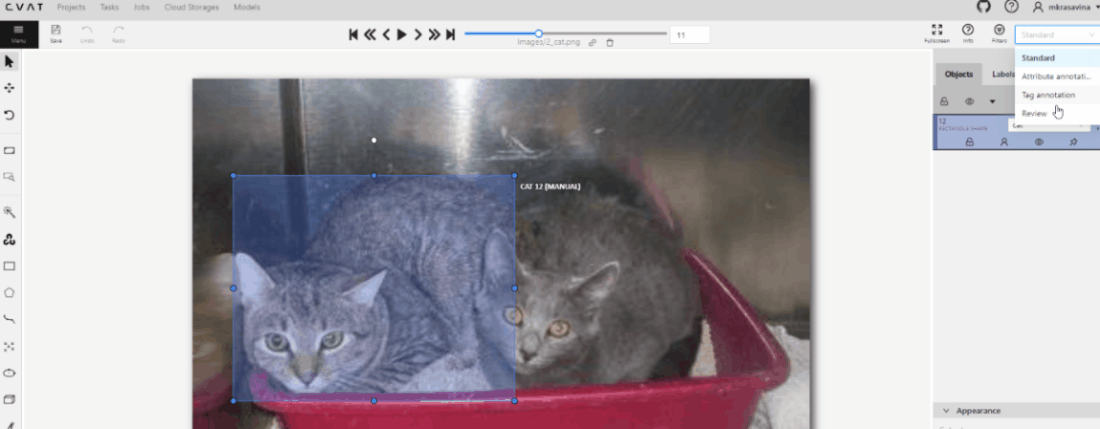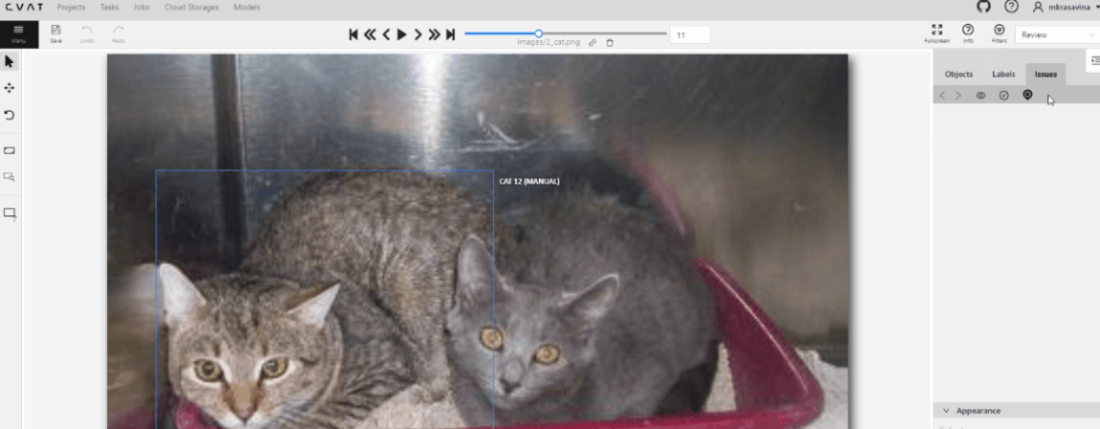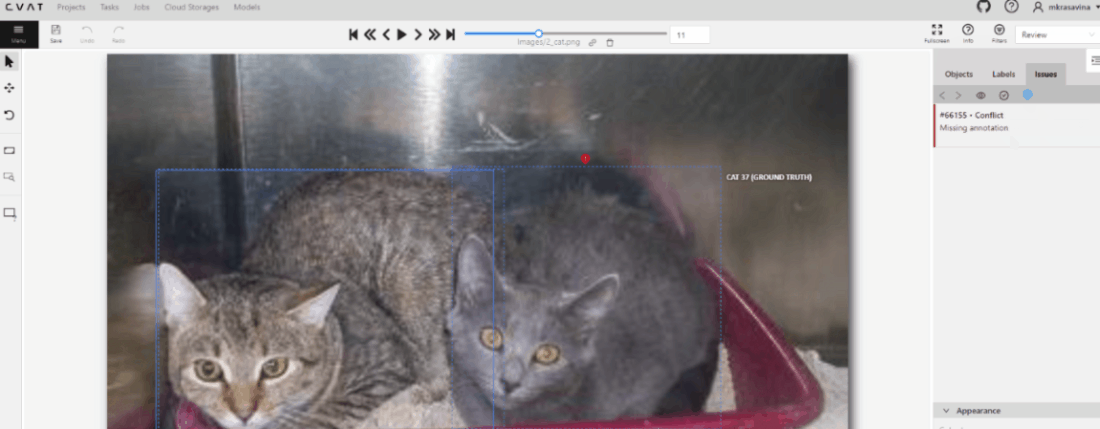
The ground truth (GT) annotation is depicted as a dotted-line box with an associated label.
Upon hovering over an issue on the right-side panel with your mouse, the corresponding GT Annotation gets highlighted.
Use arrows in the Issue toolbar to move between GT conflicts.
To create an issue related to the conflict, right-click on the bounding box and from the menu select the type of issue you want to create.
Annotation quality & Honeypot video tutorial
This video demonstrates the process: