Tasks
Overview
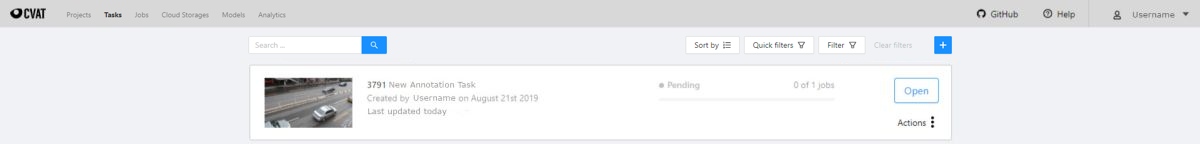
The Tasks page contains elements and each of them relates to a separate task. They are sorted in creation order.
Each element contains: the task name, preview, progress bar, button Open, and menu Actions.
Each button is responsible for a menu Actions specific function:
Export task dataset— download annotations or annotations and images in a specific format. More information is available in the export/import datasets section.Upload annotationupload annotations in a specific format. More information is available in the export/import datasets section.Automatic Annotation— automatic annotation with OpenVINO toolkit. Presence depends on how you build the CVAT instance.Backup task— make a backup of this task into a zip archive. Read more in the backup section.Move to project— Moving a task to a project (you can move only a task that does not belong to any project). In case of a label mismatch, you can create or delete necessary labels in the project/task. Some task labels can be matched with the target project labels.Organization- moving a task between your personal workspace or organizations. Only available for individual tasks (not tasks in a project). Please, refer to the Transfer between organizations section for details.Delete— delete task.
In the upper left corner, there is a search bar, using which you can find the task by assignee, task name etc. In the upper right corner, there are sorting, quick filters, and filter.
Filter
Note
Applying a filter disables the quick filter.The filter works similarly to the filters for annotation, you can create rules from properties, operators, and values and group rules into groups. For more details, consult the filter section. Learn more about date and time selection.
For clear all filters press Clear filters.
Supported properties for tasks list
| Properties | Supported values | Description |
|---|---|---|
Dimension |
2D or 3D |
Depends on the data format (read more in creating an annotation task) |
Status |
annotation, validation or completed |
|
Data |
video, images |
Depends on the data format (read more in creating an annotation task) |
Subset |
test, train, validation or custom subset |
learn more |
Assignee |
username | Assignee is the user who is working on the project, task or job (they are specified on task page) |
Owner |
username | The user who owns the project, task, or job |
Last updated |
last modified date and time (or value range) | The date can be entered in the dd.MM.yyyy HH:mm format or by selecting the date in the window that appears when you click on the input field |
ID |
number or range of job ID | |
Project ID |
number or range of project ID | |
Name |
name | On the tasks page: name of the task, on the project page: name of the project |
Project name |
project name | Specified when creating a project, can be changed on the (project section) |
Select Open to go to task details.
Task details page
Task details is a task page that contains a preview, a progress bar, the details of the task (specified when the task was created), and the Jobs section.
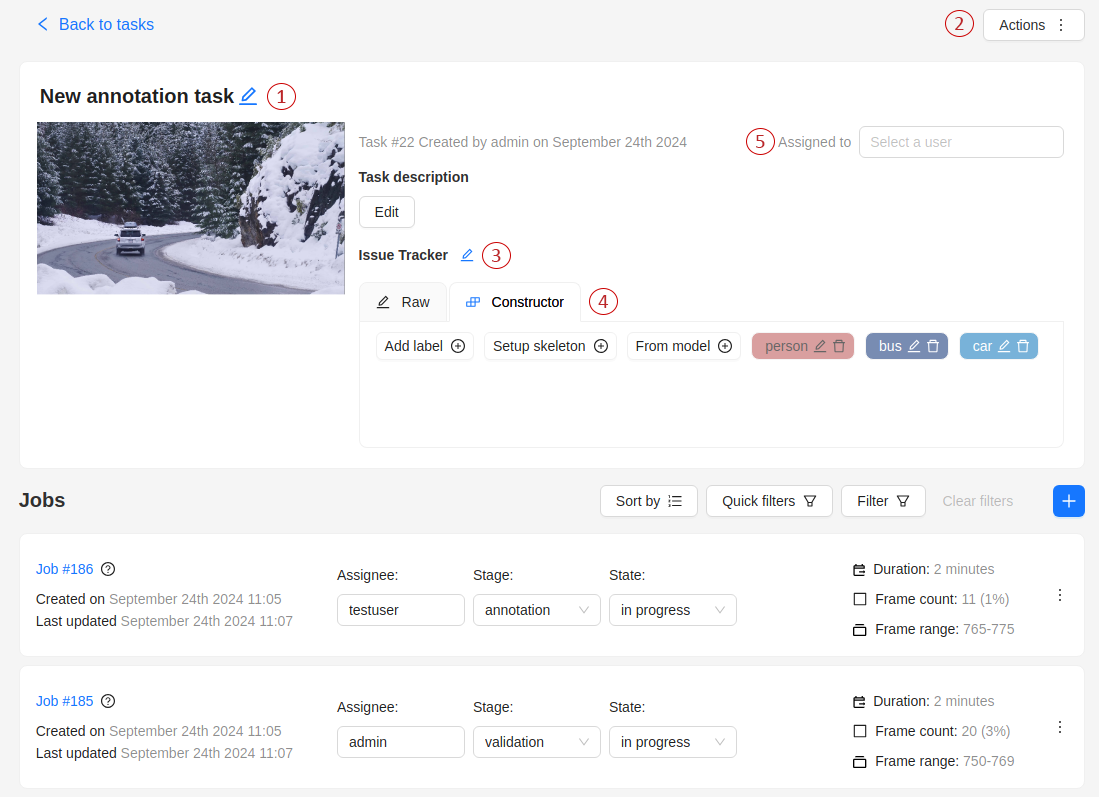
The next actions are available on this page:
-
Change the task’s title.
-
Open
Actionsmenu. -
Change the issue tracker or open it if specified.
-
Change labels (available only if the task is not related to the project).
You can add new labels or add attributes for the existing labels in the Raw mode or the Constructor mode. By selecting
Copyyou will copy the labels to the clipboard. -
Assigned to — is used to assign a task to a person. Start typing an assignee’s name and/or choose the right person out of the dropdown list. In the list of users, you will only see the users of the organization where the task is created.
-
Cloud storage — view the cloud storage attached to the task and change it to another attached storage if needed.
Jobs is a list of all jobs for a particular task. Here you can find the next data:
- Jobs name with a hyperlink to it.
- Frame range — the frame interval.
- A stage of the job. The stage is specified by a drop-down list.
There are three stages:
annotation,validation, oracceptance. This value affects the task progress bar. - A state of the job. The state can be changed by an assigned user in the menu inside the job.
There are several possible states:
new,in progress,rejected,completed. - Duration — is the amount of time the job is being worked.
- Assignee is the user who is working on the job (annotator, reviewer, or corrector). You can start typing an assignee’s name and/or choose the right person out of the dropdown list.
You can filter or sort jobs by status, assignee, and updated date using the filters panel.
Follow a link inside Jobs section to start the annotation process. In some cases, you can have several links. It depends on the size of your task and Overlap Size and Segment Size parameters. To improve UX, only the first chunk of several frames will be loaded and you will be able to annotate the first images. Other frames will be loaded in the background.
How to create and configure an annotation task
To start annotating in CVAT, you must create an annotation task and specify its parameters.
Create a task
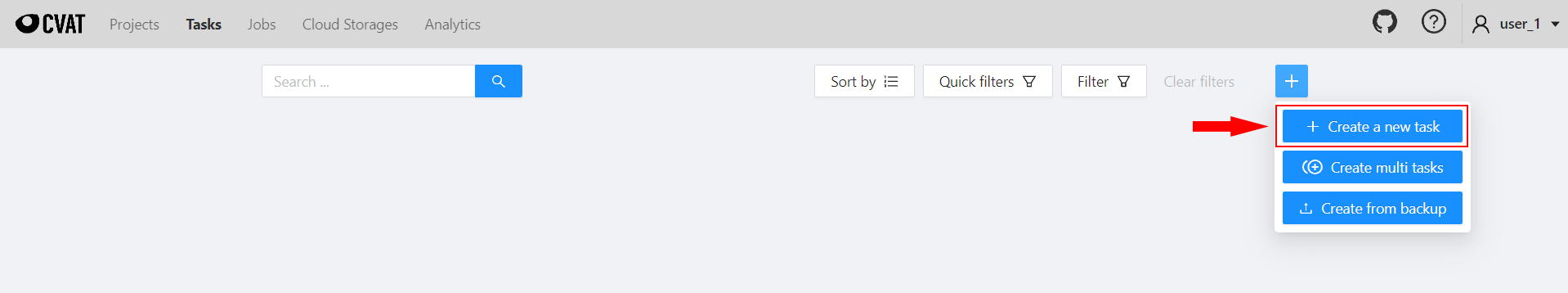
To create a task:
- On the Tasks page, select +
- Select Create new task.
Next, specify the task parameters in the configurator:
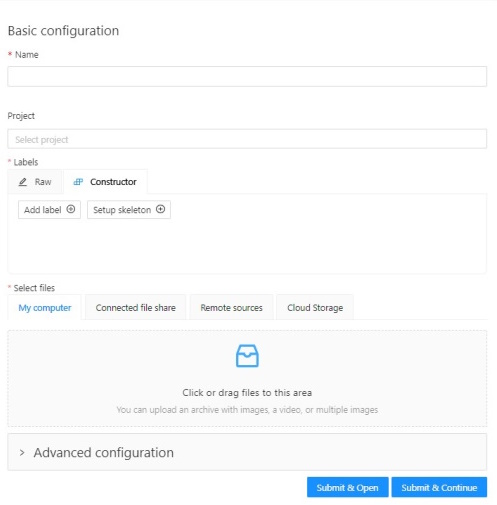
-
In the Name field, enter the name of the new task.
-
(Optional) From the Projects drop-down, select a project for the new task.
Leave this field empty if you do not want to assign the task to any project.
Note
Following steps are valid if the task does not belong to a project.
If the task has been assigned to a project, the project’s labels will be applied to the task. -
On the Constructor tab, select Add label.
The label constructor menu will open: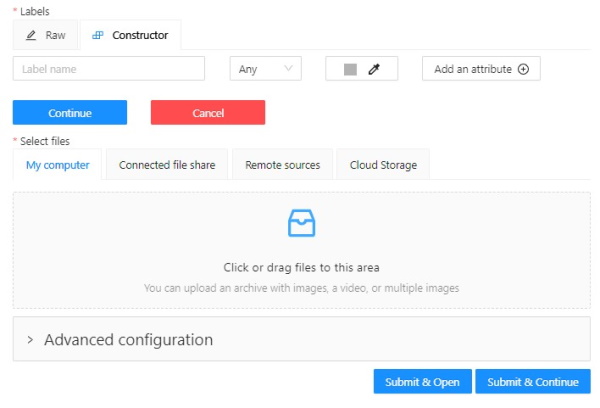
-
In the Label name field, enter the name of the label.
-
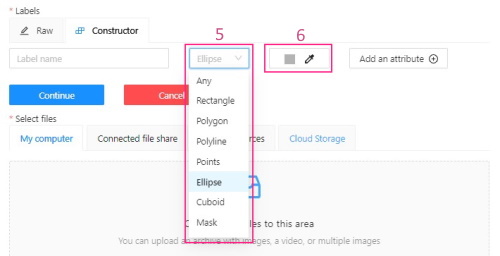
(Optional) To limit the use of the label to a certain shape tool, from the Label shape drop-down select the shape.
-
(Optional) Select the color for the label.
-
(Optional) Select Add an attribute and set up its properties.
-
Select Select files to upload files for annotation.
-
Select Continue to submit the label and start adding a new one
or Cancel to terminate the current label and return you to the labels list. -
Select Submit and open to submit the configuration and open the created task,
or Submit and continue, to submit the configuration and start a new task.
Label shape
Labels (or classes) are categories of objects that you can annotate.
Label shape limits the use of the label to certain shape tool.
Any is the default setting that does not limit the use of the
label to any particular shape tool.
For example, if you added:
- Label
sunwith the Label shape typeellipse - Label
carwith the Label shape typeany
As a result:
-
The
sunlabel will be available only for ellipse shape. -
The
carlabel will be available for all shapes.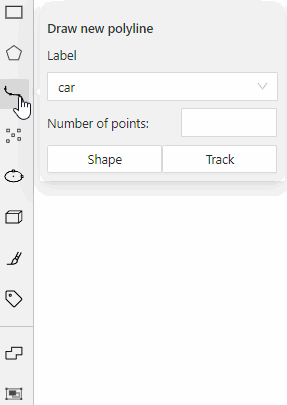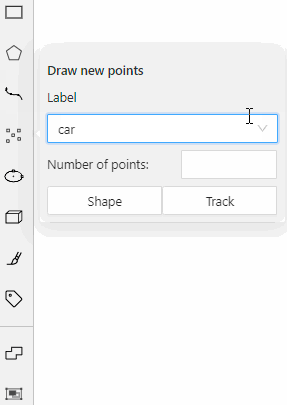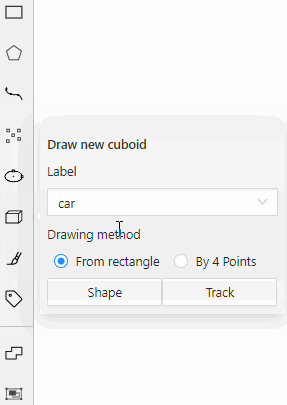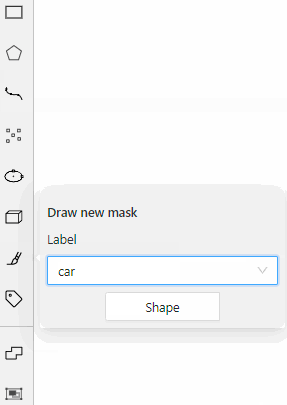
The tools on the Controls sidebar will be limited to the selected types of shapes.
For example, if you select Any,
all tools will be available,
but if you select Rectangle for all labels,
only the Rectangle tool will be
visible on the sidebar.
Note
You cannot apply the Label shape to the AI and OpenCV tools, these tools will always be available.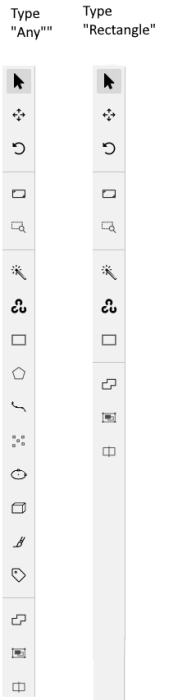
You can change the shape of the label as needed. This change will not affect the existing annotation.
For example, if you created objects using polygons and then changed the label shape to polylines, all previously created objects will remain polygons. However, you will not be able to add new polygon objects with the same label.
Note
You cannot change the shape of theskeleton label.
The Label shape field for the
skeleton label is disabled.
Add an attribute
Attribute is a property of an annotated object, such as color, model, or other quality.
For example, you have a label for face and want to
specify the type of face. Instead of creating additional
labels for male and female, you can use attributes
to add this information.
There are two types of attributes:
- Immutable attributes are unique and do not change from frame to frame.
For example,
age,gender, andcolor. - Mutable attributes are temporary and can change from frame to frame.
For example,
pose,quality, andtruncated.
Added attributes will be available from the Objects menu:
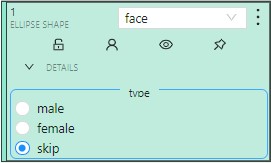
To add an attribute:
-
Go to the Constructor tab and select Add attribute.
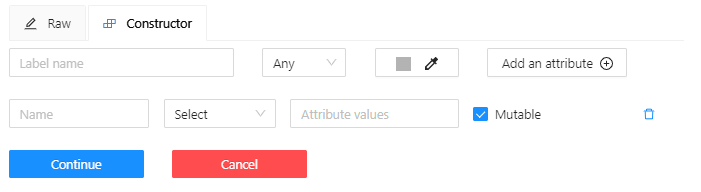
-
In the Name field, enter the attribute name.
-
In the drop-down menu, select the way to display the attribute in the Objects menu:
-
Selectenables a drop-down list, from which you can select an attribute.
If in the Attribute value field you add__undefined__, the drop-down list will have a blank value.
This is useful for cases where the attribute of the object cannot be clarified: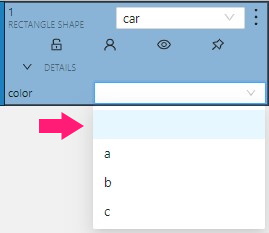
-
Radioenables the selection of one option from several options. -
Checkboxenables the selection of multiple options. -
Textsets the attribute to a text field. -
Numbersets the attribute to numerical field in the following format:min;max;step.
-
-
In the Attribute values field, add attribute values.
To separate values use Enter.
To delete value, use Backspace or click x next to the value name. -
(Optional) For mutable attributes, select Mutable.
-
(Optional) To set an attribute value as default, select it. The default value will change color to blue.
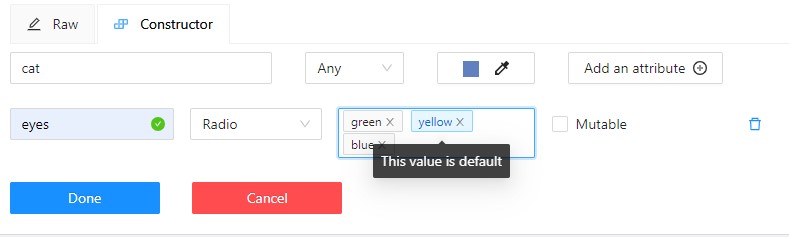
To delete an attribute, select Delete attribute.
Select files
There are several ways to upload files:
| Data source | Description |
|---|---|
| My computer | Use this option to select files from your laptop or PC. To select file: 1. Select Select files field:  . . 2. Select files to upload. |
| Connected file share | Advanced option. Upload files from a local or cloud shared folder. Note, that you need to mount a fileshare first. For more information, consult Share path |
| Remote source | Enter a list of URLs (one per line) in the field. |
| Cloud Storage | Advanced option. To upload files from cloud storage, type the cloud storage name, (optional) choose the manifest file, and select the required files. For more information, consult Attach cloud storage. Use the search feature to find a file (by file name) from the connected cloud storage. |
Editing labels in RAW format
The Raw is a way of working with labels for an advanced user.
It is useful when you need to copy labels from one independent task to another.
Note
Be careful with changing the raw specification of an existing task/project. Removing any “id” properties will lead to losing existing annotations. This property will be removed automatically from any text you insert to this field.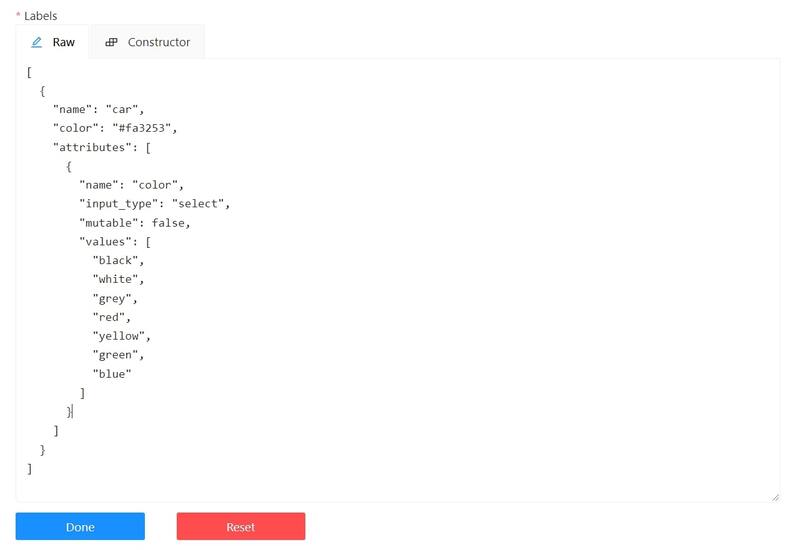
Raw presents label data in .json format with an option of editing and copying labels as text. The Done button applies the changes and the Reset button cancels the changes.
Data formats for a 3D task
To create a 3D task, you must prepare an archive with one of the following directory structures.
Note
You can’t mix 2D and 3D data in the same task. VELODYNE FORMAT
Structure:
velodyne_points/
data/
image_01.bin
IMAGE_00 # unknown dirname,
# generally image_01.png can be under IMAGE_00, IMAGE_01, IMAGE_02, IMAGE_03, etc
data/
image_01.png 3D POINTCLOUD DATA FORMAT
Structure:
pointcloud/
00001.pcd
related_images/
00001_pcd/
image_01.png # or any other image 3D, DEFAULT DATAFORMAT Option 1
Structure:
data/
image.pcd
image.png 3D, DEFAULT DATAFORMAT Option 2
Structure:
data/
image_1/
image_1.pcd
context_1.png # or any other name
context_2.jpgAdvanced configuration
Use advanced configuration to set additional parameters for the task and customize it to meet specific needs or requirements.
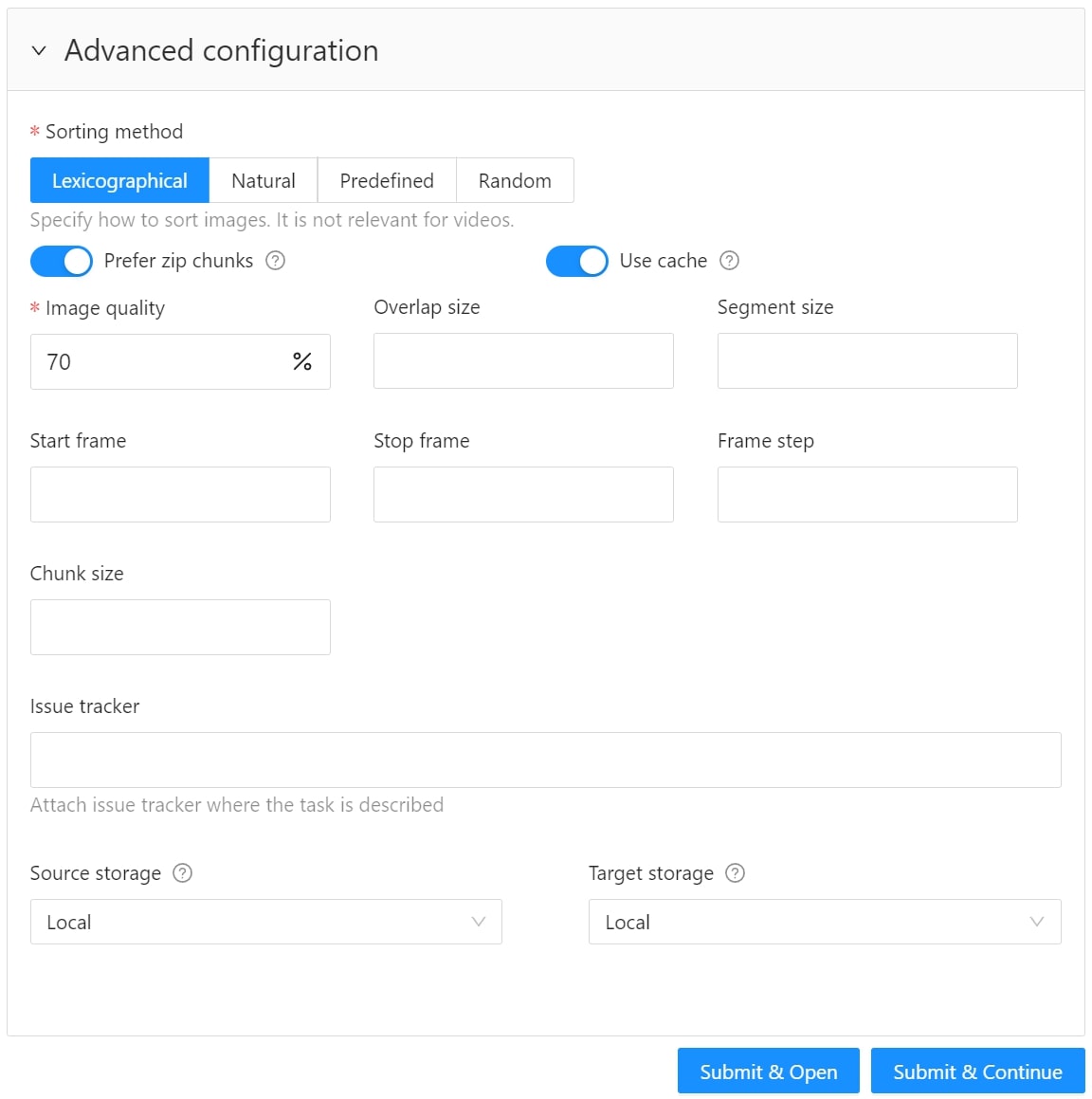
The following parameters are available:
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Sorting method | Note: Does not work for the video data. Several methods to sort the data. For example, the sequence 2.jpeg, 10.jpeg, 1.jpeg after sorting will be: 1.jpeg, 10.jpeg, 2.jpeg 1.jpeg, 2.jpeg, 10.jpeg 2.jpeg, 10.jpeg, 1.jpeg |
| Prefer zip chunks | Use this parameter to divide your video or image dataset for annotation into short video clips a zip file of frames. Zip files are larger but do not require decoding on the client side, and video clips are smaller but require decoding. It is recommended to turn off this parameter for video tasks to reduce traffic between the client side and the server. |
| Use cache | Select the checkbox to enable on-the-fly data processing to reduce task creation time and store data in a cache with a policy of evicting less popular items. For more information, see Data preparation on the fly. |
| Image quality | CVAT has two types of data: original quality and compressed. Original quality images are used for dataset export and automatic annotation. Compressed images are used only for annotations to reduce traffic between the server and client side. It is recommended to adjust the compression level only if the images contain small objects that are not visible in the original quality. Values range from 5 (highly compressed images) to 100 (not compressed). |
| Overlap size | Use this parameter to create overlapped segments, making tracking continuous from one segment to another. Note that this functionality only works for bounding boxes. This parameter has the following options: Interpolation task (video sequence). If you annotate with a bounding box on two adjacent segments, they will be merged into a single bounding box. In case the overlap is zero or the bounding box is inaccurate (not enclosing the object properly, misaligned or distorted) on the adjacent segments, it may be difficult to accurately interpolate the object’s movement between the segments. As a result, multiple tracks will be created for the same object. Annotation task (independent images). If an object exists on overlapped segments with overlap greater than zero, and the annotation of these segments is done properly, then the segments will be automatically merged into a single object. If the overlap is zero or the annotation is inaccurate (not enclosing the object properly, misaligned, distorted) on the adjacent segments, it may be difficult to accurately track the object. As a result, multiple bounding boxes will be created for the same object. If the annotations on different segments (on overlapped frames) are very different, you will have two shapes for the same object. To avoid this, accurately annotate the object on the first segment and the same object on the second segment to create a track between two annotations. |
| Segment size | Use this parameter to divide a dataset into smaller parts. For example, if you want to share a dataset among multiple annotators, you can split it into smaller sections and assign each section to a separate job. This allows annotators to work on the same dataset concurrently. |
| Start frame | Defines the first frame of the video. |
| Stop frame | Defines the last frame of the video. |
| Frame step | Use this parameter to filter video frames or images in a dataset. Specify frame step value to include only certain frames or images in the dataset. For example, if the frame step value is 25, the dataset will include every 25th frame or image. If a video has 100 frames, setting the frame step to 25 will include only frames 1, 26, 51, 76, and 100 in the dataset. This can be useful for reducing the size of the dataset, or for focusing on specific frames or images of particular interest. |
| Chunk size | Defines amount of frames to be packed in a chunk when send from client to server. The server defines automatically if the chunk is empty. Recommended values: |
| Issue tracker | Use this parameter to specify the issue tracker URL. |
| Source storage | Specify the source storage for importing resources like annotations and backups. If the task was assigned to the project, use the Use project source storage toggle to determine whether to use project values or specify new ones. |
| Target storage | Specify the target storage (local or cloud) for exporting resources like annotations and backups. If the task is created in the project, use the Use project target storage toggle to determine whether to use project values or specify new ones. |
To save and open the task, select Submit & Open .
To create several tasks in sequence, select Submit & Continue.
Created tasks will be displayed on the tasks page.
How to create and set up multiple tasks
Use Create multi tasks to create multiple video annotation tasks with the same configuration.
Note
The Create multi tasks feature is available for videos only.Check out:
Create multi tasks
To create the multi tasks:
- On the Tasks page select +.
- Select Create multi tasks.
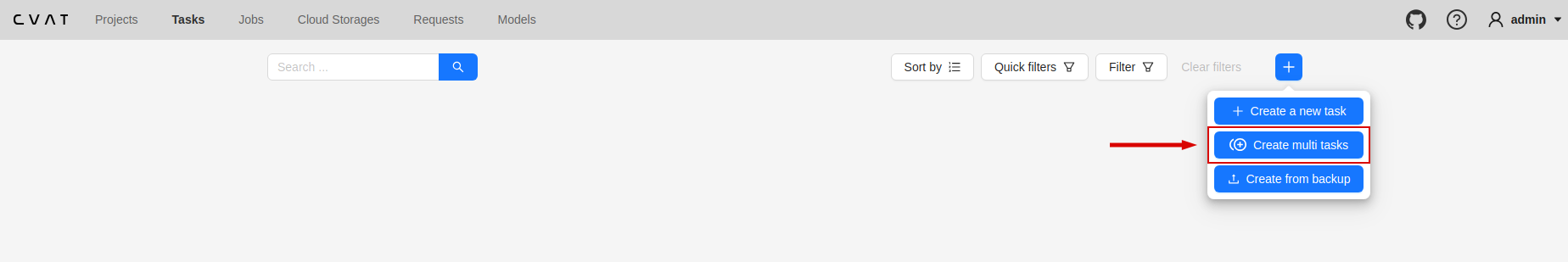
Next, specify the parameters in the task configurator:
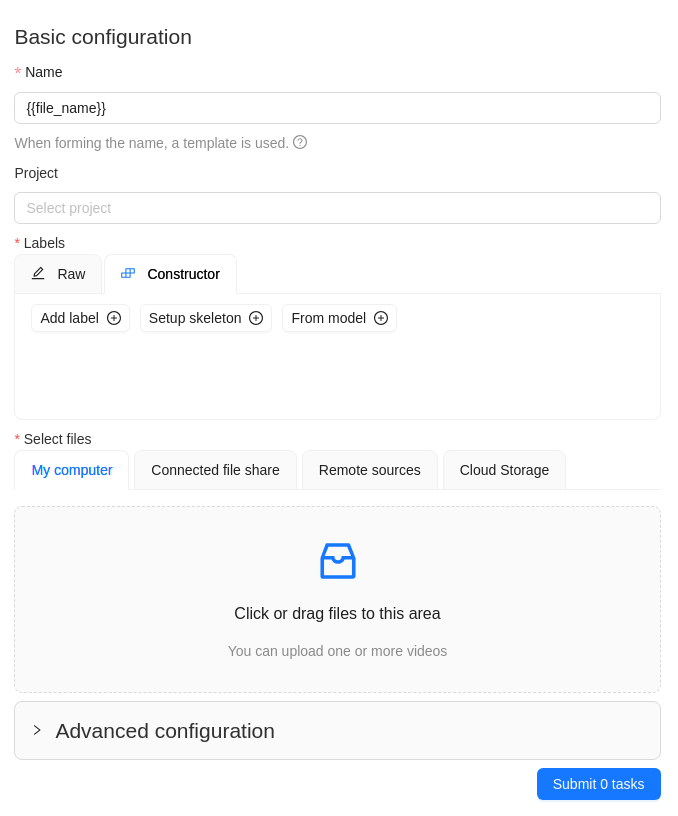
-
In the Name field, enter the name of the new task:
- Enter the name of the task
- (Optional)
{{index}}adds an index to the file in the set (starting from 0). - (Optional)
{{file_name}}adds the file’s name to the task’s name.
-
(Optional) From the Projects drop-down, select a project for the tasks.
Leave this field empty if you do not want to assign tasks to any project.
Note
Following steps are valid if the tasks do not belong to a project.
If the tasks have been assigned to a project, the project’s labels will be applied to the tasks. -
On the Constructor tab, select Add label.
-
In the Label name field, enter the name of the label.
-
(Optional) Select the color for the label.
-
(Optional) Select Add an attribute and set up its properties.
-
Select Select files to upload files for annotation.
Note
You cannot upload multiple tasks from the cloud storage. -
Select Submit
Ntasks
Example
A step-by-step example for creating the multiple tasks:
-
In the Name field, enter the
Create_multitask-{{index}}-{{file_name}}. -
Add labels.
-
Select files.
In case there are more than four files, only the total number of selected files will be displayed: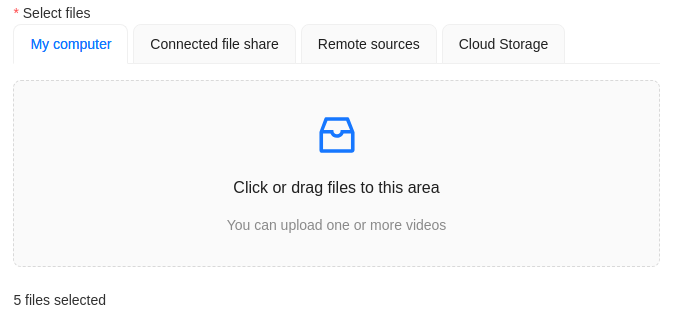
-
Select Submit
Ntasks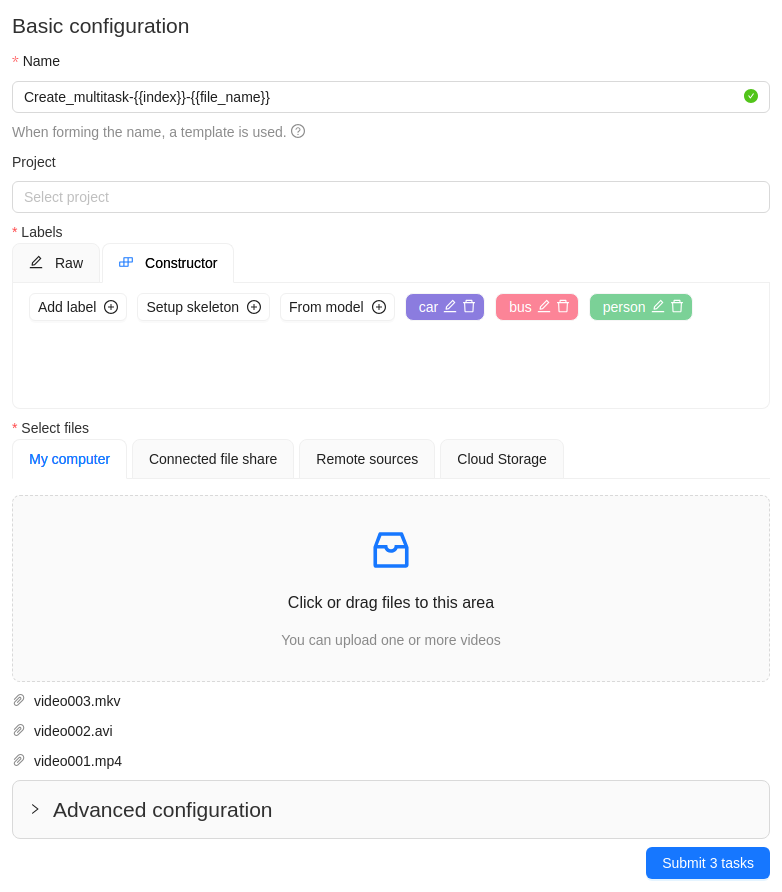
-
You will see a progress bar that shows the progress of the tasks being created:
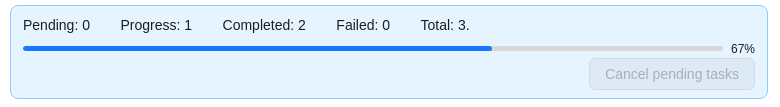
-
Select Ok.
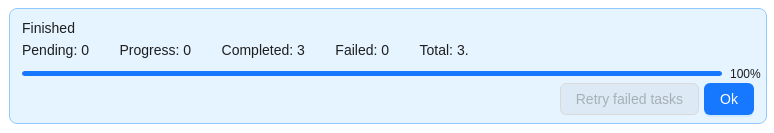
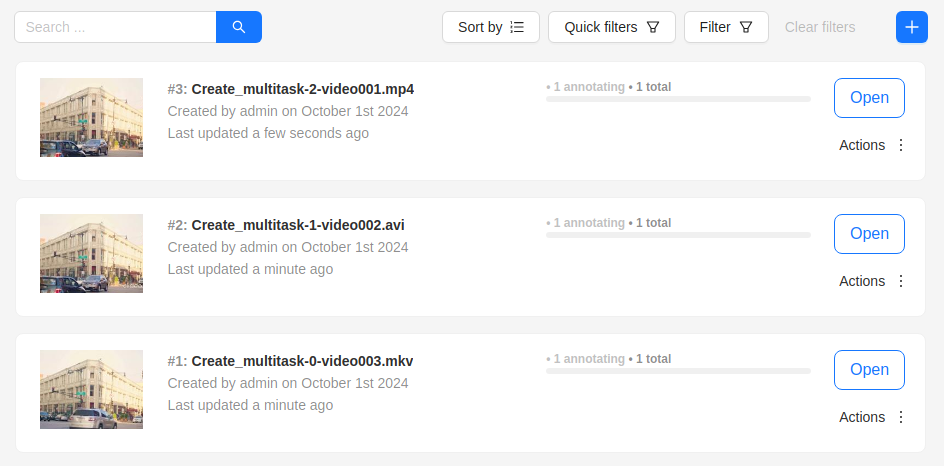
The result will look like the following:
Errors
During the process of adding multiple tasks, the following errors may occur:
| Error | Description |
|---|---|
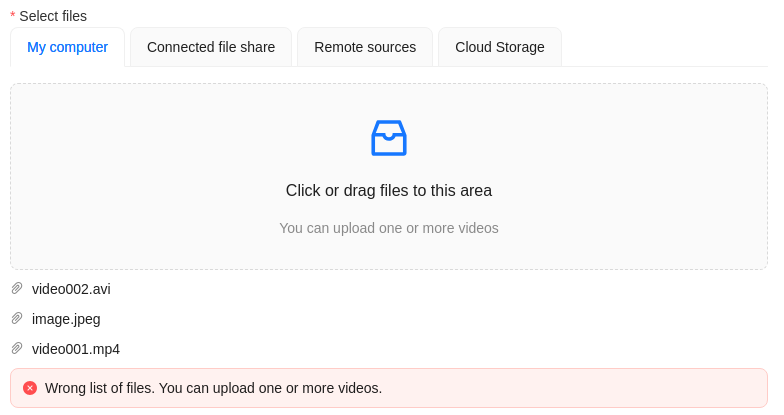 |
Wrong file format. You can add only video files. |
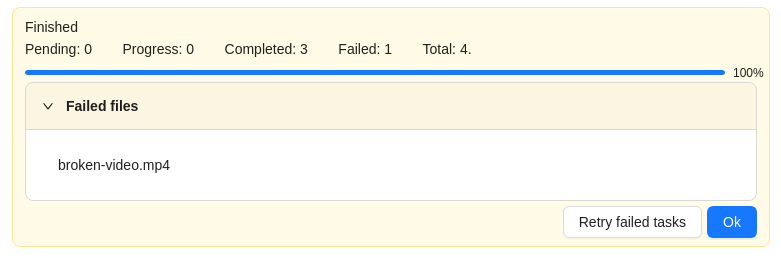 |
In the process of creating a task, CVAT was not able to process the video file. The name of the failed file will be displayed on the progress bar. To fix this issue: |
Advanced configuration
Use advanced configuration to set additional parameters for the task and customize it to meet specific needs or requirements.
For more information, consult Advanced configuration
How to delete a frame from a task
You can delete the current frame from a task. This frame will not be presented either in the UI or in the exported annotation. Thus, it is possible to mark corrupted frames that are not subject to annotation.
-
Go to the Job annotation view and click on the Delete frame button (Alt+Del).
Note
When you delete with the shortcut, the frame will be deleted immediately without additional confirmation.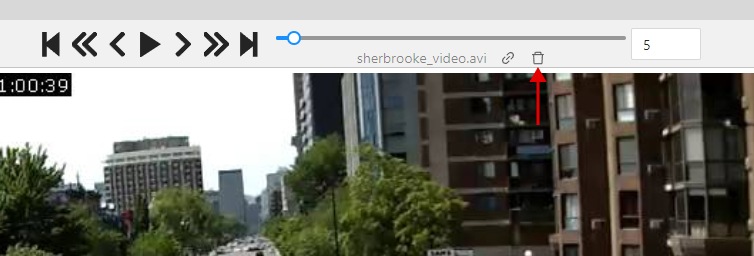
-
After that you will be asked to confirm frame deleting.
Note
all annotations from that frame will be deleted, unsaved annotations will be saved and the frame will be invisible in the annotation view (Until you make it visible in the settings). If there is some overlap in the task and the deleted frame falls within this interval, then this will cause this frame to become unavailable in another job as well. -
When you delete a frame in a job with tracks, you may need to adjust some tracks manually. Common adjustments are:
- Add keyframes at the edges of the deleted interval for the interpolation to look correct;
- Move the keyframe start or end keyframe to the correct side of the deleted interval.
Configure deleted frames visibility and navigation
If you need to enable showing the deleted frames, you can do it in the settings.
-
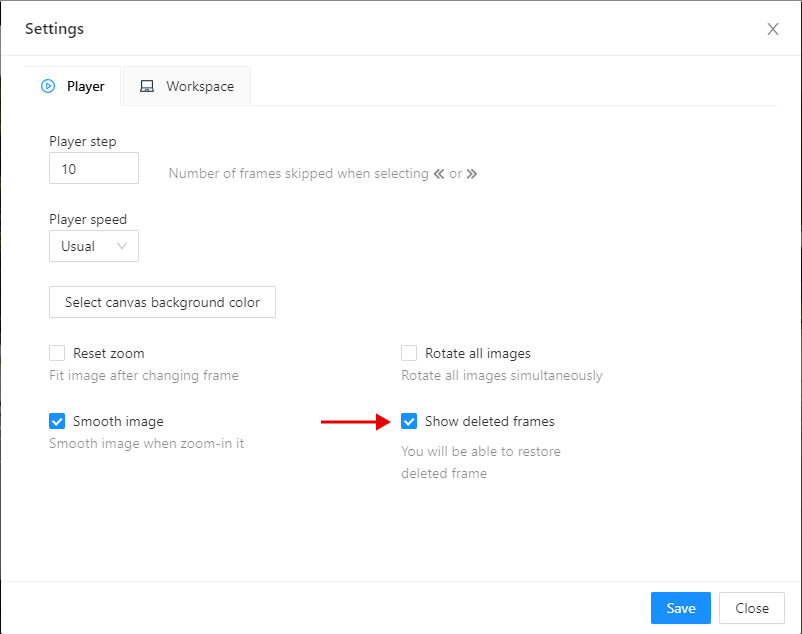
Go to the settings and chose Player settings.
-
Click on the Show deleted frames checkbox. And close the settings dialog.

-
Then you will be able to navigate through deleted frames. But annotation tools will be unavailable. Deleted frames differ in the corresponding overlay.
-
There are ways to navigate through deleted frames without enabling this option:
- Go to the frame via direct navigation methods: navigation slider or frame input field,
- Go to the frame via the direct link, for example:
/api/tasks/{id}/jobs/{id}?frame={frame_id}.
-
Navigation with step will not count deleted frames.
Restore deleted frame
You can also restore deleted frames in the task.
-
Turn on deleted frames visibility, as it was told in the previous part, and go to the deleted frame you want to restore.
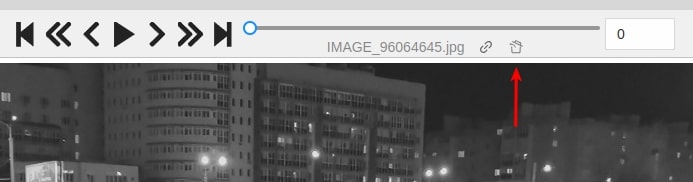
-
Click on the Restore icon. The frame will be restored immediately.